Our Strengths
Safety for natural disasters
Japan has been exposed to various natural disasters such as flood, landslide, earthquake, scouring, windstorm, and snowstorm. Their damaging effects have intensified recently. JR East has ample experience and knowledge to restrict and resume railway operations smoothly as a result of natural disasters. The following systems are utilized in preparation for disasters.
Operation with Prevention of Disaster Alarm System
JR East has developed an original system called PreDAS (Prevention of Disaster Alarm System) to obtain weather information from seismographs, rain gauges, and anemometers. To prevent trains from entering areas where natural disasters may arise, we have defined certain thresholds for rainfall, wind speed, and seismic intensity. When the measured value exceeds the thresholds, operations are suspended, or speed is restricted.
Train Operation Restrictions Using Precipitation Radar
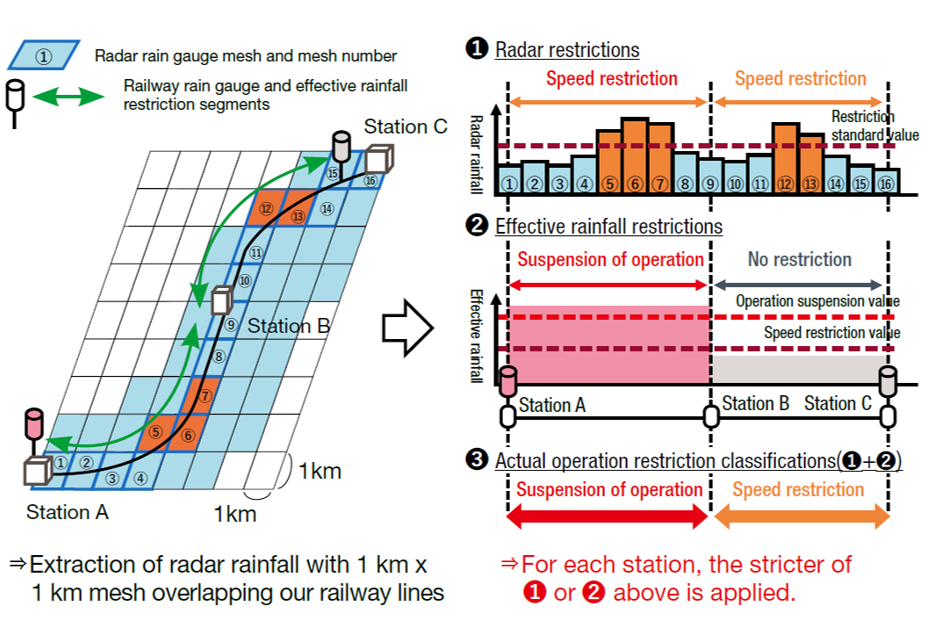
In recent years, rainfall disasters have become more severe and frequent, and localized heavy rains are increasing. In June 2023, JR East introduced new operational regulations using a precipitation radar to PreDAS on conventional lines. They can inspect localized heavy rainfall in areas without rain gauges and enable us to deal with severe rainfall.
Rolling stock Evacuation Judgment Support System
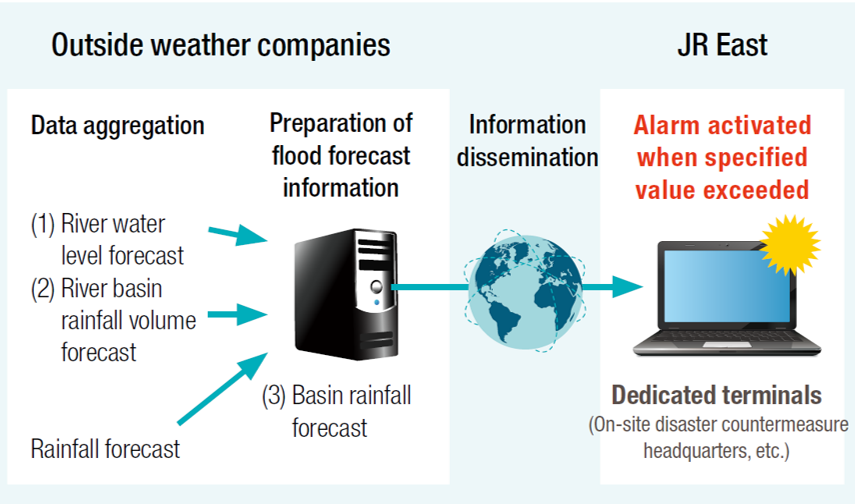
JR East has introduced a Rolling stock Evacuation Judgment Support System at depots facing a risk of flooding to promptly evacuate rolling stock upon disaster. With this system, we have developed indexes to support decisions on rolling stock evacuation. When each indicator reaches the set value, personnel will receive notification.
Windbreak fence

JR East has vast experience and knowledge to select areas where high winds could derail and overturn the train, and to regulate operations based on wind speed. Windbreak fences have been installed to decrease the number of service disruptions caused by strong winds. As a result, the frequency of service disruption caused by strong winds has reduced. On the Keiyo Line connecting Tokyo and Chiba, the number of suspended operation hours has dropped by 55% and the number of speed restriction hours has fell by 61%.
JR East will contribute to the safe railway operation against natural disasters by providing our disaster management technologies as well as knowledge, such as standard development, education and training programs to global railway operators.
JR East's advanced disaster management technology helps to make the global railway operations safer.
Future Prospects

Futoshi MITSUHATA
Deputy Director
Global Railway Business Department
International Affairs Headquarters, JR East
After working for an engineering and consulting firm, he joined JR East in 2011. With his extensive experience on railway improvement projects, he was seconded to JICA to promote railway ODA projects. He has passionately devoted himself to developing our international business since his return to JR East.

JR East operates in areas with a variety of transportation needs, from the Tokyo metropolitan area, which boasts one of the world's largest numbers of railway passengers, from regional cities where road transportation is the dominant mode to mountainous areas where the population is declining. Our business areas are also characterized by the risk of natural disasters such as earthquakes, typhoons, and heavy snowfall. To address these challenges, we proactively incorporate the latest technologies, such as digital transformation (DX), to provide rail transportation services tailored to each business environment.
Railways are operated or planned in various business environments globally. We provide worldwide railway operators with optimal solutions in all phases of railway planning, construction, and operations and maintenance (O&M) by utilizing our technologies and experience to meet the unique challenges of each environment.
Smart Maintenance
for Rolling Stock
JR East is continually carrying out condition-based maintenance (CBM) and risk-based maintenance (RBM). These maintenance methods lead to higher reliability and lower maintenance costs.
-

CBM on Commuter Train
- Monitors and analyzes big data to assess the condition of rolling stock and detect potential defects to prevent failure.
- Identifies signs of failure and take preventive actions to minimize the possibilities of failure.
-

RBM for Purple Line in Thailand
- Evaluate the risk of breakdowns and perform maintenance at appropriate intervals.
- Contribute to the provision of reliable railway transportation services.
- Achieved no serious incidents reported in 2023.
for Infrastructures
Innovative equipment installed in not only inspection cars but also passenger cars collects various data. Analyzing this data enables efficient maintenance.
-
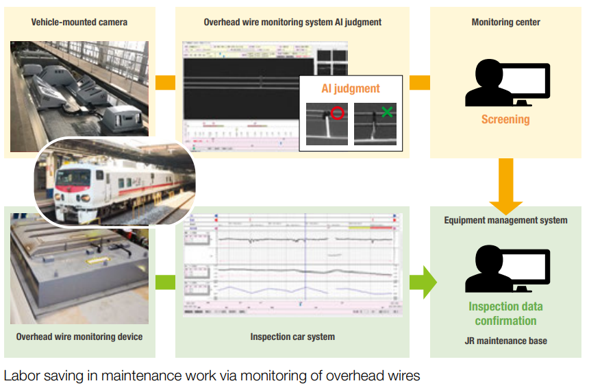
Inspection car with monitoring function
- This inspection car is installed with cameras and sensors that capture images and other data of the catenary and track.
- AI-based image recognition has been introduced.
-
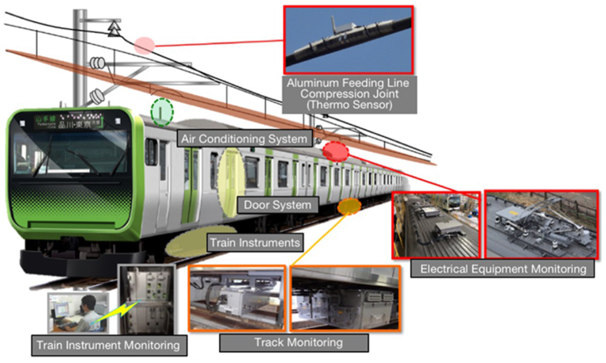
Passenger car with monitoring function
- The catenary and track inspection equipment installed in passenger cars continuously collect various data during service operation.
- This allows for a rapid response before a serious failure arises, improving reliability and saving labor.
- AI supports our work.
Energy and Environment
Clean Energy Rolling Stock
JR East has unveiled its innovative Clean Energy Rolling Stock, which utilizes battery and hydrogen fuel cell technology as a sustainable alternative to diesel power. Currently, JR East has battery-powered trains in service and is conducting trials of hydrogen fuel cell-powered trains on active service lines.
-

Rolling Stock Powered by Battery
- Reduce CO2 emission by 60% and noise by 30 dB compared to conventional diesel rolling stock.
-

Rolling Stock Powered by Hydrogen Fuel Cell
- Zero CO2 emission during operation.
- Maximum Speed: 100 km/h
The Stations Utilizing Natural Resource

(Tokyo, opened in 2020)
To reduce CO2 emissions, JR East utilizes the natural resources and renewable energies for stations.
For example, Takanawa Gateway Station in Tokyo features a roof made from a special membrane designed to maximize sunlight utilization. This innovative membrane also has a self-cleaning function, activated by rain and sunlight. In addition, the station utilizes sea wind for energy generation, taking advantage of its unique waterfront location.
For another example, Musashi-Mizonokuchi Station in Kawasaki utilizes CO2-free hydrogen as a power source for lighting during regular operations. In the event of a disaster, a power supply is available to essential facilities at the station, allowing it to serve as a temporary shelter using stored hydrogen to power fuel cells.
Energy-saving Operation
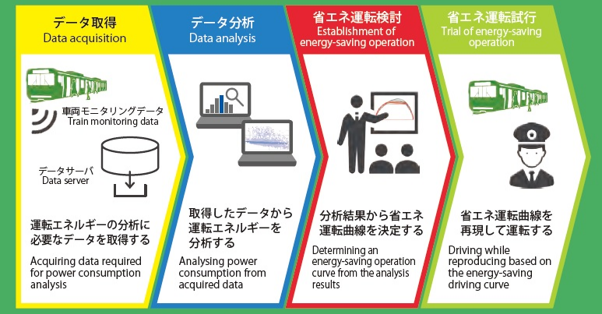

JR East has developed an energy-saving operation by analyzing operation data on the existing line. This innovative approach leads to reduction in operational energy consumption by an average of 13.7%* when the drivers follow this analysis-based pattern.
*: This value referred from trial on the Yamanote Line.
Mega Railway Projects
JR East, with state-of-the-art techniques in engineering and project management, has successfully completed mega railway infrastructure projects with minimum impact on railway operations and services.
Major Station Reformation
Shibuya Station, a large-scale terminal serviced by 4 private railway companies with 9 lines, plays a key role for a public transportation node, boasting nearly 310,000 passengers daily on the JR East Lines. Station facilities have been repeatedly expanded and renovated in line with the development of the surrounding area. These changes eventually led to a less user-friendly station due to complicated transfers, aging station facilities, and lack of barrier-free routes. To address these issues, JR East implemented drastic improvements toward its functions, including parallelization and expansion of the platforms while maintaining scheduled services. The relocation of the Saikyo Line platform required minimal service suspension only for 2 days.
-
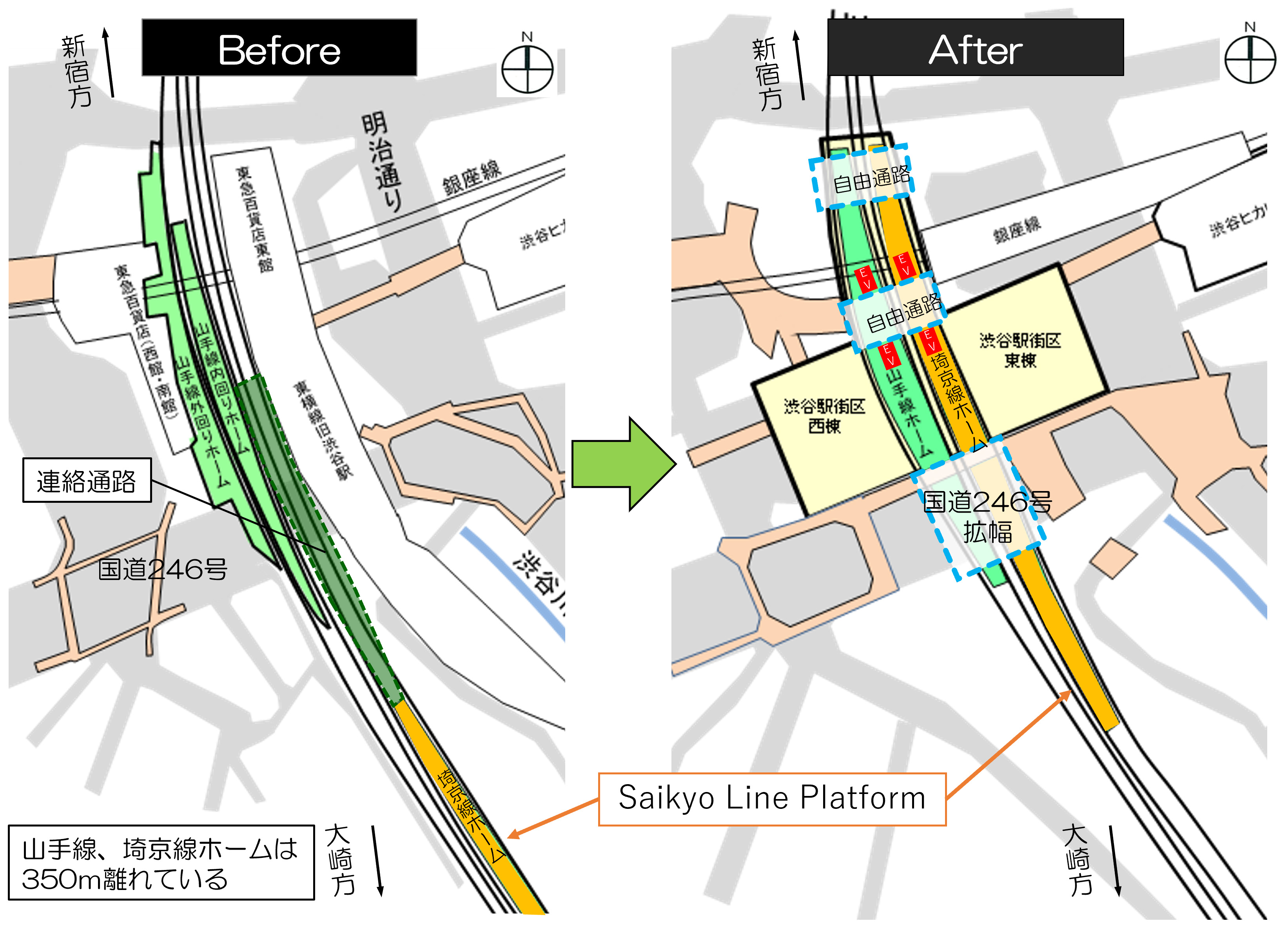
Scale of the Saikyo Line Platform Relocation -

New Line Development Over Existing Line
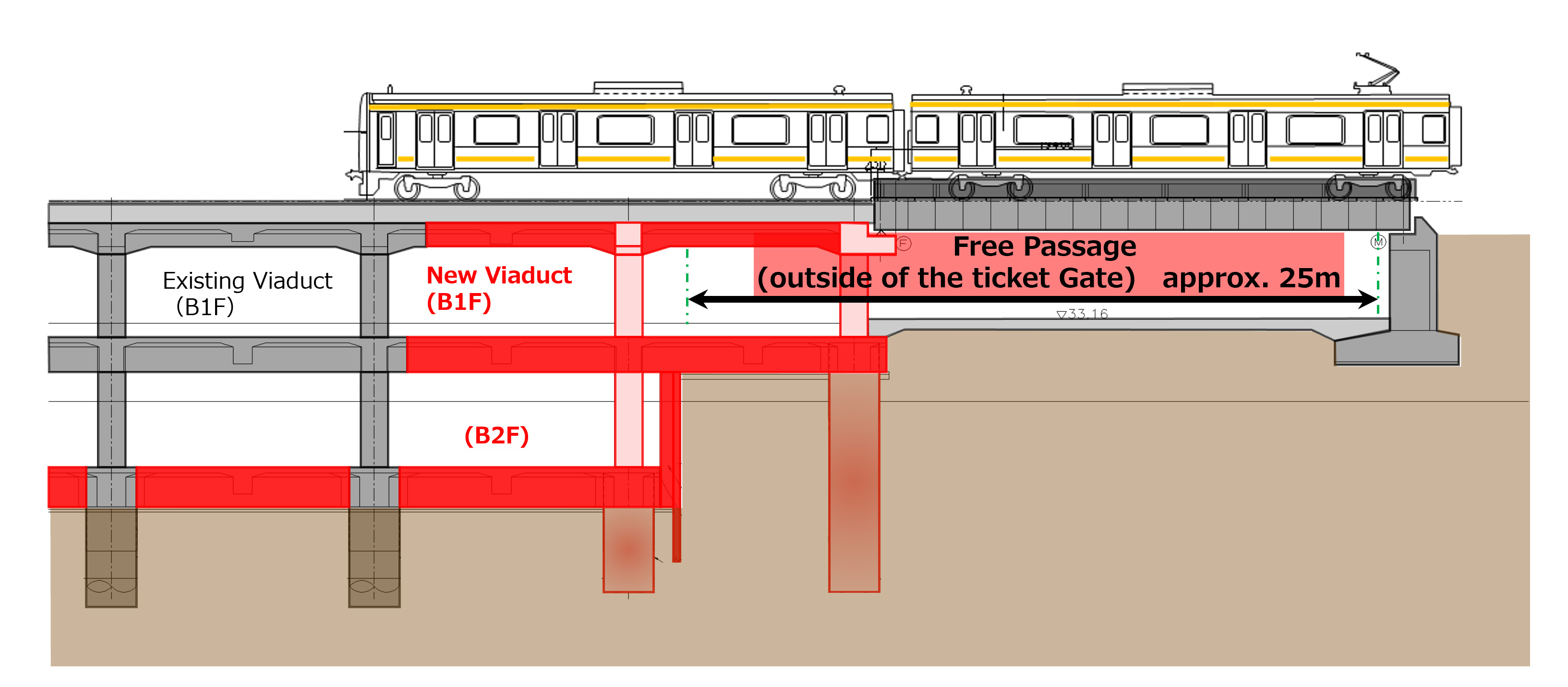
The Ueno-Tokyo Line construction project involved constructing a new conventional line in the narrow construction space of central Tokyo. This transportation improvement project aimed to open a new through operation route on the trunk line connecting the north and south of the metropolitan region. The construction of the new line contributed to easing passenger congestion, reducing travel time and strengthening the railway network. In some sections, JR East effectively completed the highly challenging task of constructing new viaducts over the existing railway lines while they were still in service.
-
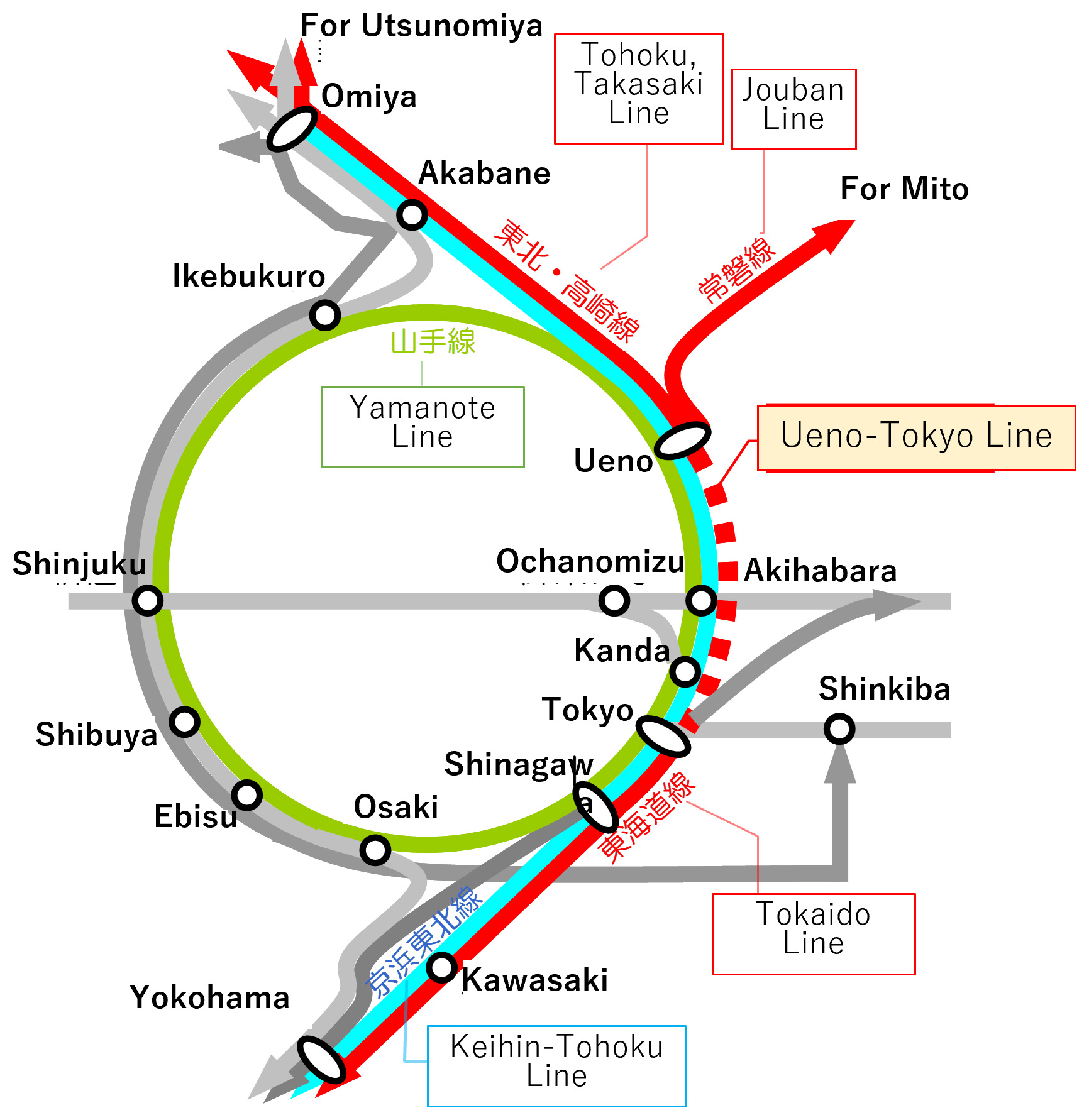
The Ueno-Tokyo Line Construction Project -
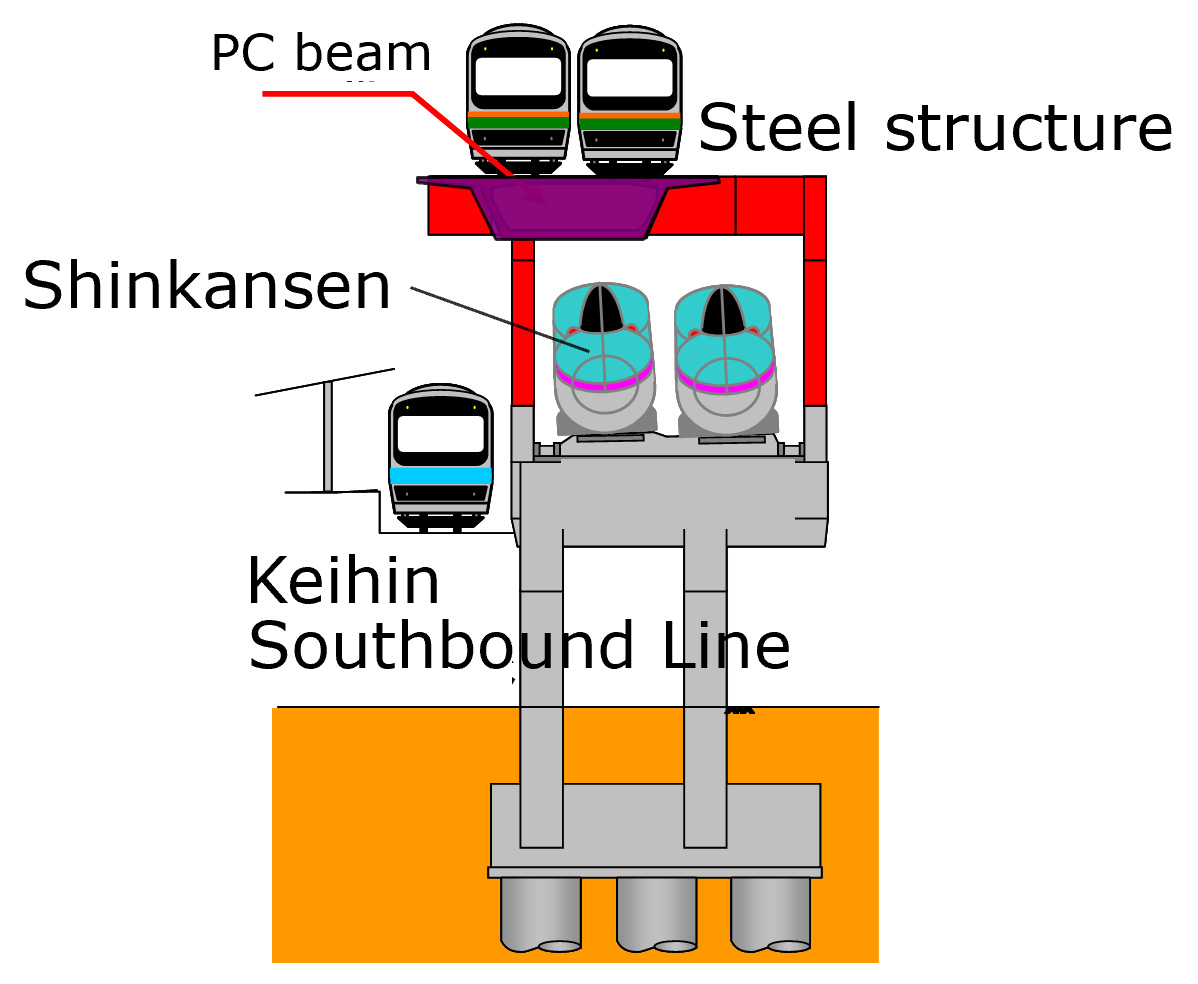
Cross-Sectional Diagram -

Project Above the Operating Railway
Expansion of the Busiest Station
Shinjuku Station is one of the world's busiest terminal stations, with 3 million passengers passing through daily. To improve the station’s pedestrian circulation and public transportation node function, JR East implemented a project to install a public concourse under the 8-platform and 16-track station to connect the east and west sides of the station. In addition, an artificial ground was constructed over the railway tracks. Our advanced project management has sustained socio-economic activities without interruption, while ensuring the daily safety and stability of our railway operations.